LED: Light Emitting Diode (LED) Light Emitting Diode (LED) comprises several layers of semiconducting material. When the diode is being utilized with DC, the active layer produces light. The LED emits light in a particular color and this color is dependent on the type of semiconductor material used in it. LEDs are made of semiconductor crystals. When current flows through the crystals, they emit light in red, green, yellow or blue colors depending on the composition of the crystal compounds. Blue LEDs also emit white light by using a yellowish fluorescent layer or by creating a mix of red, green and blue (RGB) LEDs.
Components of an LED
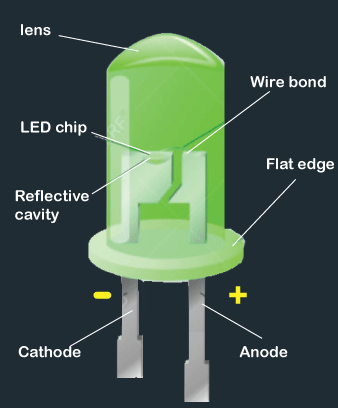
The components of the LED are listed below:
- Lens
The lens in an LED is used to evenly distribute the light. - LED Chip
LED chips are the small yellow piece that creates light. It is attached to the piece of metal. - Reflective Cavity
The reflective cavity is the surface cavity that ensures the direction of light. It converges the light to maintain its brightness. - Flat Edge
The flat edge of an LED prevents the leads from twisting. The current passes through the lead that causes the LED to glow. Hence, it is essential to prevent the leads from any twisting. - Wire bond
Wire bonding is an essential part of an LED that connects the LED chips. It also provides an electrical connection between the lead frame and the Light Emitting chips. - Semiconductor diode
The semiconductor diode is a p-n junction material, which is coated with impurities. The impurities excite the electron that causes the LED to glow. The ability of LEDs to become heavily doped is one of the important factors for its wide applications. The material used for the fabrication of LEDs and band gap determines the radiation it can emit. For example, GaAs (Gallium-Arsenic) is used as a material for infrared radiations. - Two leads or terminals
The LED has two terminals called cathode (negative) and anode (positive). The anode is the longer lead, while the cathode is the shorter lead of an LED.
Colored LED
LED's are available in different colors. Let's discuss different colored LEDs and the concept behind their colored lights. The variation in the concentration of phosphors can cause a change in the color temperature. Phosphor is defined as a substance present over a semiconductor die used to display the property of luminescence. The phosphor is responsible for the colored lights in the LED. There are around 16 million shades of LEDs.
So, let's discuss different colored lights and the concept behind their colored lighting.
White LED
White light can be formed in two ways. One way is to produce the three colored lights (Red, Green, and Blue) and combine them. Another way is called Fluorescence, which is defined as a process in which a phosphor coating converts one colored light to another colored light. For example, blue light to white light.
Blue LED
A fluorescent chemical present in the bulb is used to convert the white light into blue light. The chemical is called Gallium Nitride. Blue LED is considered the best light to possess anti-bacterial properties.
Red LED
The material used for red LED lights is called Gallium Arsenide Phosphorus (GaAsP). It is a semiconductor material.
Green LED
Some manufacturers use phosphor material on the blue light to convert it into green light. The phosphor materials are used to convert the high energy spectrum into low energy.
RGB LED
RGB (Red, Green, and Blue) LED is a combination of the three different basic colors LED. Other colors are formed from these three basic colors only. The brightness and intensity of these three colors can be changed to produce a different color.

0 Comments